Smart Robot Monitor with AI Alerts
Introduction
This tutorial demonstrates how to integrate Vultr, MindsDB, and Gemini API to build an intelligent robot monitoring system that generates natural language maintenance reports. You'll simulate robot telemetry, store it in PostgreSQL, and use AI to generate maintenance reports and a chatbot that answers questions about your fleet.
This stack is particularly valuable for AI hackathons, where you need to prototype quickly and showcase a working demo. Whether you're in online AI hackathons or virtual AI hackathons, having a clear data pipeline plus an AI agent gives judges a strong, demo-ready project. If you're looking for upcoming AI hackathons to try this out, explore LabLab.ai's global AI hackathons.
What You'll Build
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have created a complete AI-powered monitoring system that:
- Simulates real-time robot telemetry data (battery, temperature, status)
- Stores data in a PostgreSQL database hosted on Vultr
- Uses MindsDB to connect AI models to your database
- Generates natural language maintenance reports using Google Gemini
- Provides an intelligent chatbot agent to query your robot fleet data
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have:
- Repository – Clone smart-robot-monitor-with-AI-alerts to get the full project (simulator, database schema, MindsDB scripts,
requirements.txt, and.env.example). - Vultr Account - Sign up at vultr.com and add a payment method
- MindsDB - We'll install this via Docker in the tutorial
- Google Gemini API Key - Get one free at Google AI Studio
- Docker - Install from docker.com
- Basic Knowledge - Familiarity with SQL, Python, and command line basics
- Python 3.8+ - Installed on your local machine
Part 1: Understanding the Python Robot Simulator
To keep this tutorial practical, we'll simulate robot telemetry data using Python rather than connecting to actual physical robots. This simulator mimics real-world robot behavior and continuously sends data to your database—ideal for AI hackathon projects where you need a working demo without physical hardware.
What the Simulator Does
The simulator generates realistic robot telemetry with the following features:
Core Functionality:
- Battery Monitoring: Simulates gradual battery drain from 100% down to 0%, then auto-recharges
- Temperature Tracking: Generates realistic temperature readings using normal distribution (fluctuates around 55°C)
- Status Codes: Assigns integer codes representing robot health (0=OK, 1=WARNING, 2=ERROR)
- Anomaly Injection: Randomly introduces problems like low battery or overheating (configurable probability)
- Real-time Logging: Displays color-coded status indicators in your terminal
- Auto-reconnect: Handles database connection failures gracefully
Technical Details:
- Data Generation Rate: Configurable interval (default: every 5 seconds)
- Battery Drain Rate: 0.5% per reading by default
- Anomaly Probability: 15% chance of introducing an anomaly
- Temperature Range: 40-70°C under normal conditions, can spike to 95°C during anomalies
- Database: Uses PostgreSQL with automatic transaction handling
The simulator consists of three main files in the simulator/ directory:
robot_simulator.py- Main simulator script with database connectivityconfig.py- Configuration settings loaded from environment variables__init__.py- Python package initialization
📁 View the complete simulator code: simulator/
How It Works
The simulator operates in a continuous loop:
- Generate Data: Creates battery and temperature readings with realistic fluctuations
- Inject Anomalies: Randomly introduces issues based on configured probability
- Determine Status: Evaluates readings and assigns status codes (OK/WARNING/ERROR)
- Store in Database: Inserts telemetry into PostgreSQL with automatic retries
- Log Output: Displays formatted readings with visual indicators (✅ OK, ⚠️ WARNING, 🚨 ERROR)
- Wait: Pauses for the configured interval before the next reading
When battery reaches 0%, it automatically recharges to 100% to enable continuous testing.
Part 2: Setting Up Vultr & Creating the PostgreSQL Database
Vultr will host both our PostgreSQL database and MindsDB instance in the cloud, making them accessible from anywhere.
Step 2.1: Deploy Your Vultr Server
-
Navigate to Vultr Dashboard Go to my.vultr.com/dashboard and click the "Deploy +" button in the top right corner.
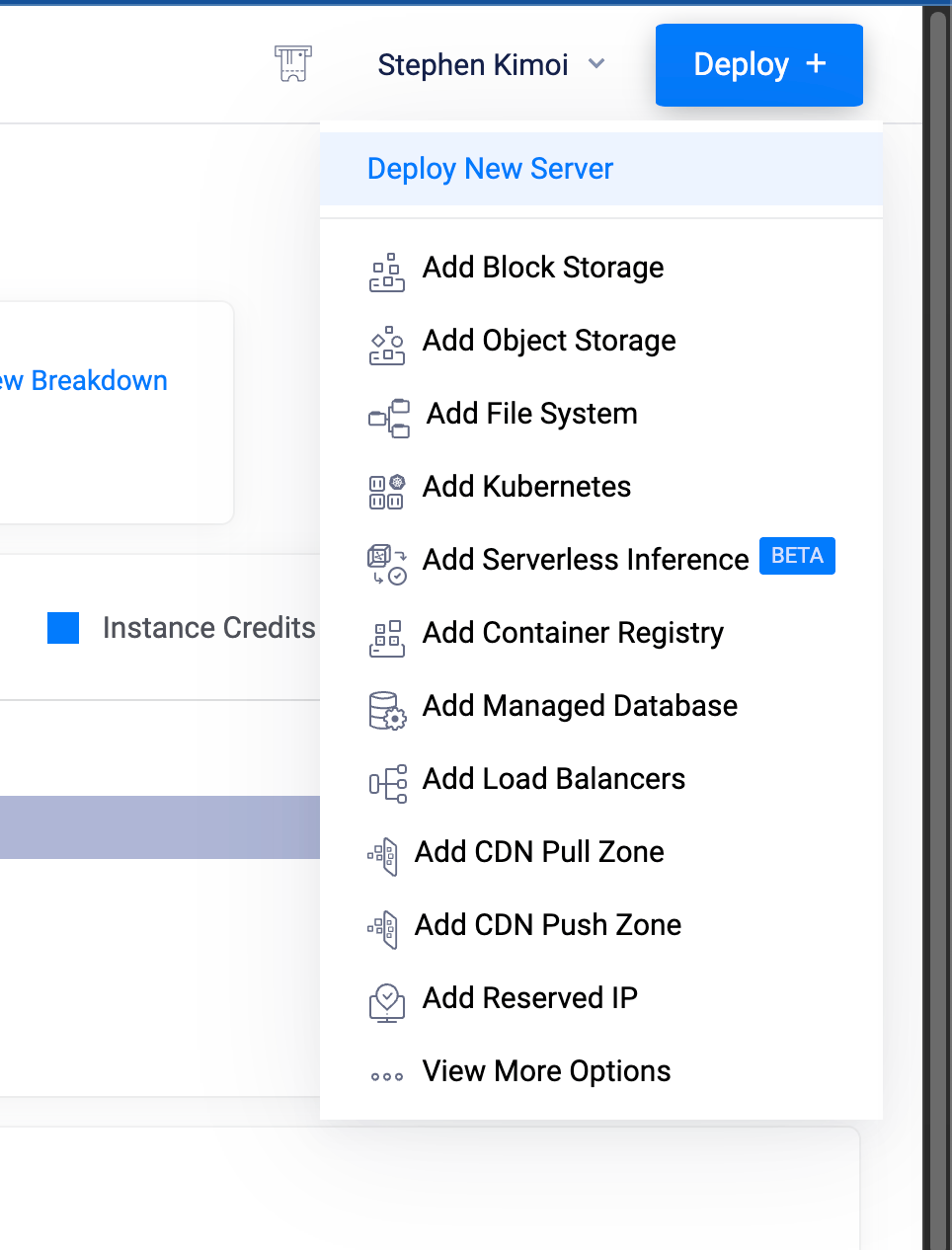
Deploy a server -
Choose Server Type
- Select "Cloud Compute" for a standard virtual machine
- Choose "Ubuntu 22.04 LTS" as your operating system
-
Select Server Location Pick a data center closest to your location for better latency
-
Choose Server Size
- For this tutorial, a $6/month plan (1 CPU, 1GB RAM) is sufficient
- You can scale up later if needed
-
Add SSH Key (Recommended) If you have an SSH key, add it for secure access. Otherwise, you'll receive a root password via email.
-
Configure Additional Settings
- Scroll down to the "Configure" section
- Set a hostname like
robot-monitor-server - Enable "Auto Backups" if desired (optional, costs extra)
-
Deploy Server Click "Deploy Now" at the bottom
Note: You need to complete your profile and add a valid payment method to deploy a server.

Deploy a server configuration -
Wait for Deployment Server deployment typically takes 2-5 minutes. Once ready, you'll see the status change to "Running".
Step 2.2: Access Your Server
-
Click on your newly created server from the dashboard
-
Copy the IP Address and Password (if not using SSH keys)

Server Dashboard -
Connect via SSH:
ssh root@your-server-ip-addressEnter the password when prompted (or use your SSH key)
Step 2.3: Install PostgreSQL on Vultr
Now that you're connected to your server, let's install PostgreSQL:
# Update package lists
sudo apt update
# Install PostgreSQL
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib -y
# Start PostgreSQL service
sudo systemctl start postgresql
sudo systemctl enable postgresql
# Verify installation
sudo systemctl status postgresql
You should see "active (running)" in green.
Step 2.4: Configure PostgreSQL
# Switch to postgres user
sudo -i -u postgres
# Create the database
createdb robot_monitor_db
# Create a dedicated user
psql -c "CREATE USER robot_user WITH PASSWORD 'your_secure_password';"
# Grant privileges
psql -c "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE robot_monitor_db TO robot_user;"
# Exit postgres user
exit
Step 2.5: Create the Database Table
You can use our pre-made schema file or create it manually:
Option 1: Use the provided schema file
Get the schema from the repository (clone the repo on this server or download the file). From the repo root, run:
# Schema file is in the repo: database/setup_database.sql
sudo -u postgres psql -d robot_monitor_db -f database/setup_database.sql
📁 View the database schema:
database/setup_database.sql
Option 2: Create manually
# Create the schema file
cat > /tmp/robot_telemetry.sql << 'EOF'
-- Connect to the database
\c robot_monitor_db
-- Create the telemetry table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS robot_telemetry (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
timestamp TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT NOW(),
robot_id VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
battery_level DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL CHECK (battery_level >= 0 AND battery_level <= 100),
temperature_celsius DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL,
status_code INTEGER NOT NULL CHECK (status_code IN (0, 1, 2)),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
-- Create indexes for faster queries
CREATE INDEX idx_robot_telemetry_timestamp ON robot_telemetry(timestamp DESC);
CREATE INDEX idx_robot_telemetry_robot_id ON robot_telemetry(robot_id);
CREATE INDEX idx_robot_telemetry_status ON robot_telemetry(status_code);
-- Grant permissions to robot_user
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON TABLE robot_telemetry TO robot_user;
GRANT USAGE, SELECT ON SEQUENCE robot_telemetry_id_seq TO robot_user;
EOF
# Run the schema
sudo -u postgres psql -f /tmp/robot_telemetry.sql
Step 2.6: Configure PostgreSQL for Remote Access
By default, PostgreSQL only accepts local connections. We need to allow remote access:
# Edit PostgreSQL configuration
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/14/main/postgresql.conf
Find the line #listen_addresses = 'localhost' and change it to:
listen_addresses = '*'
Press Ctrl+X, then Y, then Enter to save.
# Edit client authentication
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/14/main/pg_hba.conf
Add this line at the end:
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
Press Ctrl+X, then Y, then Enter to save.
# Restart PostgreSQL
sudo systemctl restart postgresql
Step 2.7: Configure Firewall
# Allow PostgreSQL port
sudo ufw allow 5432/tcp
# Allow MindsDB port (we'll install this next)
sudo ufw allow 47334/tcp
# Enable firewall
sudo ufw enable
✅ Checkpoint: Your PostgreSQL database is now running on Vultr and accessible remotely.
Part 3: Connecting the Simulator to Your Vultr Database
Now let's run the robot simulator on your local machine and connect it to the database on Vultr.
Step 3.1: Set Up Your Local Environment
Clone the repository (if you haven't already), then create a virtual environment and install dependencies:
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/Stephen-Kimoi/smart-robot-monitor-with-AI-alerts.git
cd smart-robot-monitor-with-AI-alerts
# Create a virtual environment
python3 -m venv venv
# Activate it
# On macOS/Linux:
source venv/bin/activate
# On Windows:
# venv\Scripts\activate
# Install dependencies (requirements.txt is in the repo)
pip install -r requirements.txt
Step 3.2: Configure Environment Variables
# Copy the example environment file
cp .env.example .env
# Edit the .env file with your credentials
nano .env
Update the following values:
# Use your Vultr server IP address
DB_HOST=your_vultr_server_ip
DB_PORT=5432
DB_NAME=robot_monitor_db
DB_USER=robot_user
DB_PASSWORD=your_secure_password
# Robot configuration
ROBOT_ID=ROBOT-001
DATA_INTERVAL_SECONDS=5
BATTERY_DRAIN_RATE=0.5
ANOMALY_PROBABILITY=0.15
# Thresholds
BATTERY_LOW_THRESHOLD=20
TEMPERATURE_HIGH_THRESHOLD=80
# MindsDB (we'll use this later)
MINDSDB_HOST=your_vultr_server_ip
MINDSDB_PORT=47334
# Gemini API key (get from Google AI Studio)
GEMINI_API_KEY=your_gemini_api_key_here
Step 3.3: Test the Connection
# Navigate to simulator directory
cd simulator
# Run the simulator
python robot_simulator.py
Expected Output:
Initialized Robot Simulator for ROBOT-001
Configuration:
- Data interval: 5s
- Battery drain rate: 0.5% per reading
- Anomaly probability: 15.0%
- Battery anomaly threshold: <20%
- Temperature anomaly threshold: >80°C
- Database enabled: True
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Connecting to database at your_vultr_server_ip:5432...
✅ Database connection established successfully
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
🤖 Starting robot telemetry simulation...
Press Ctrl+C to stop
[0001] Robot: ROBOT-001 | Battery: 99.50% | Temp: 56.34°C | Status: ✅ OK 💾
[0002] Robot: ROBOT-001 | Battery: 99.00% | Temp: 54.21°C | Status: ✅ OK 💾
[0003] Robot: ROBOT-001 | Battery: 98.50% | Temp: 57.89°C | Status: ✅ OK 💾
The 💾 icon indicates data is being successfully stored in your database.
✅ Checkpoint: Let the simulator run for a few minutes to generate test data. You can verify by connecting to your database:
# On your Vultr server
sudo -u postgres psql -d robot_monitor_db -c "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM robot_telemetry;"
Part 4: Setting Up MindsDB
MindsDB is the bridge between your database and AI models. It allows you to query AI models using standard SQL.
Step 4.1: Install MindsDB via Docker
We'll install MindsDB on your local machine using Docker for easier setup:
-
Open Docker Desktop
-
Go to Extensions Click on the "Extensions" tab in the Docker Desktop sidebar
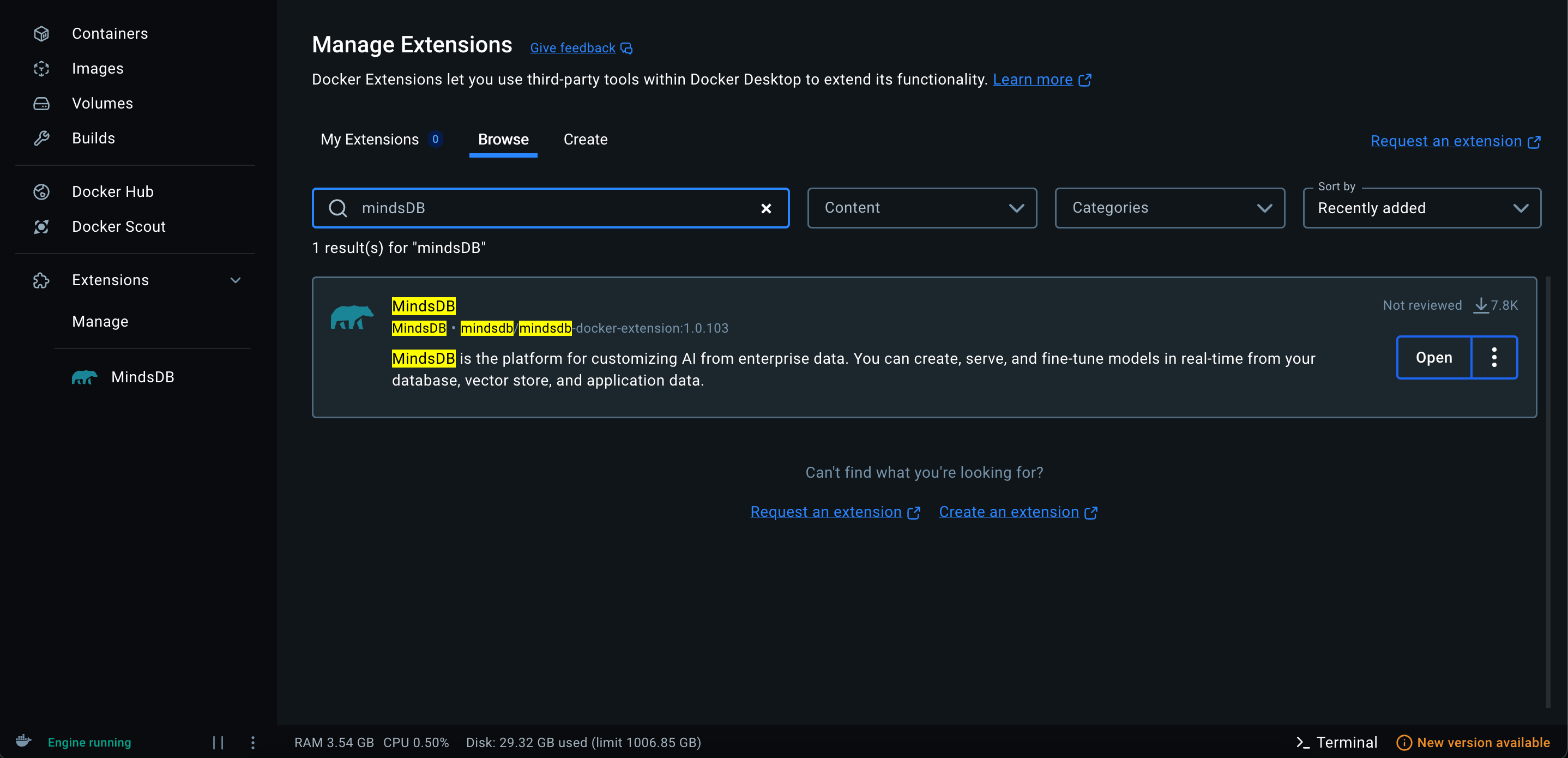
Docker MindsDB Install -
Search for MindsDB In the search bar, type "MindsDB" and click Install
-
Launch MindsDB Once installed, click "Open" to launch the MindsDB interface
Step 4.2: Complete MindsDB Onboarding
MindsDB will walk you through a quick onboarding process:
-
Welcome Screen Click "Create & Continue"

MindsDB Welcome -
Connect Data Source Click "Create & Continue" (we'll connect our actual database in a moment)
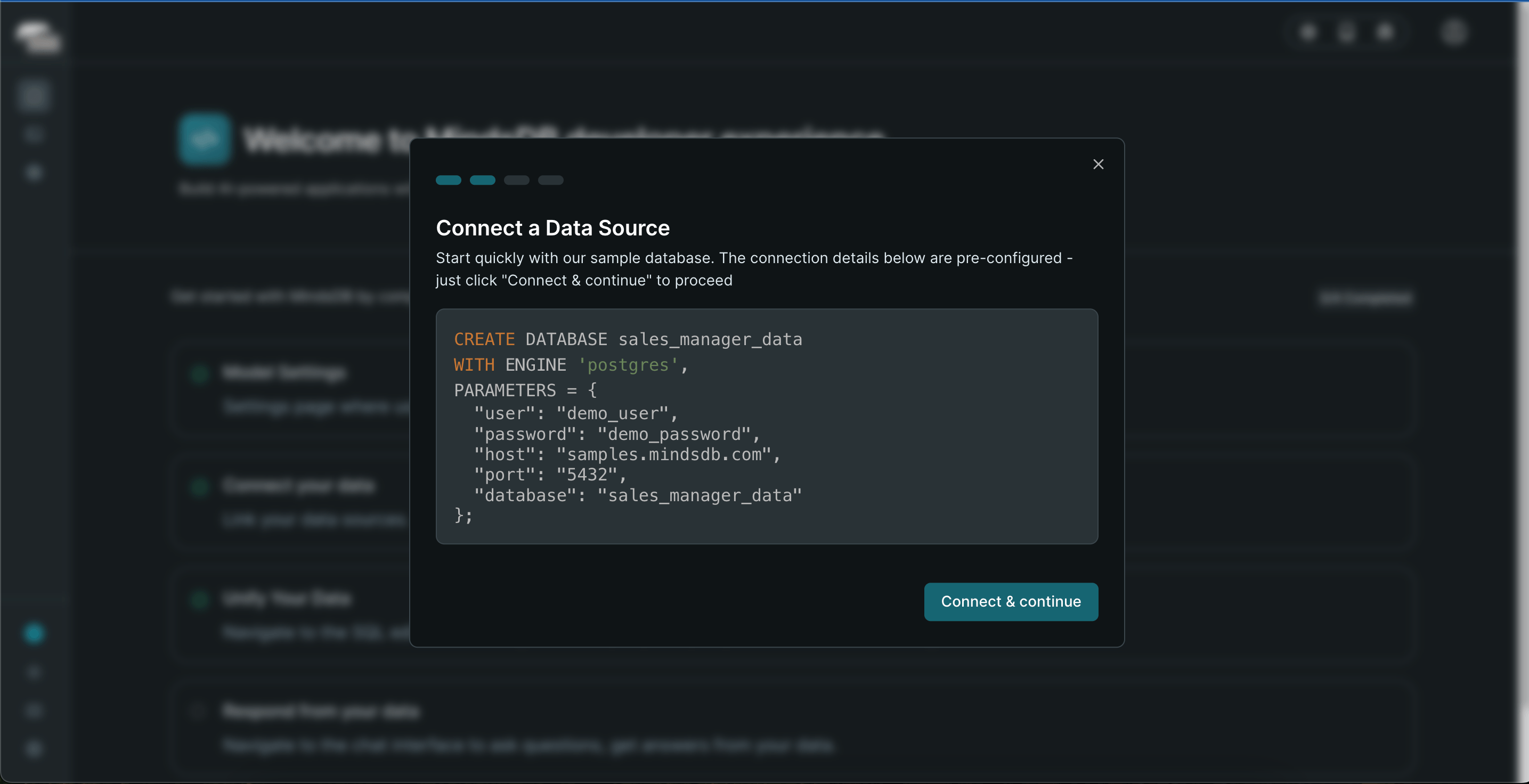
MindsDB Connect Datasource -
Create Agent Tutorial Click "Create & Continue"
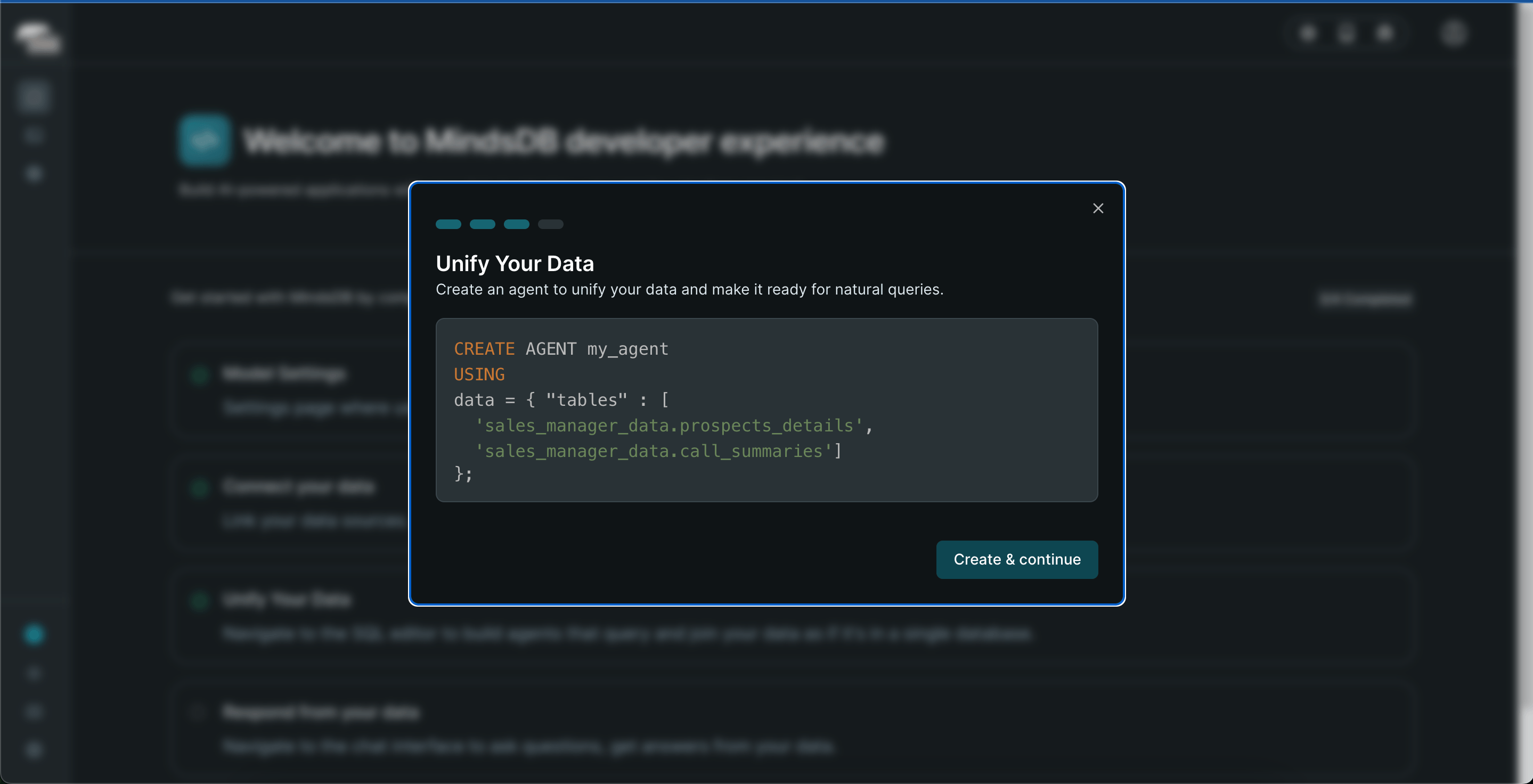
MindsDB Create an Agent Steps -
Setup Complete You'll see the main MindsDB interface
Finish setup MindsDB
Alternative Access: If you prefer not to use Docker Desktop's UI, you can access MindsDB directly at http://localhost:47334/ in your web browser.
Step 4.3: Configure Gemini API in MindsDB
Before connecting to your database, set up the Gemini AI model:
-
Get Your Gemini API Key
- Visit Google AI Studio
- Click "Create API Key"
- Copy the generated key
-
Configure in MindsDB
- In MindsDB, click the Settings icon (gear icon, top right)
- Navigate to Models > Default Model
- Select "Google" as the provider
- Enter "gemini-pro" as the model name
- Paste your API key
- Click "Save Preferences"
Step 4.4: Test MindsDB with Hello World Example
-
Open SQL Editor Click on "SQL Editor" in the left sidebar
MindsDB SQL editor -
Run the Hello World Example You'll see a pre-loaded "Hello World" tutorial. Click the green "RUN" button to execute it.

MindsDB hello world
What This Example Does:
The Hello World tutorial demonstrates MindsDB's core capabilities:
-
CONNECT: Creates a connection to a demo PostgreSQL database
CREATE DATABASE demo_db WITH ENGINE = "postgres", PARAMETERS = {...}; -
UNIFY: Transforms and enriches Amazon reviews data using AI
- Extracts product categories from product names using LLM
- Analyzes sentiment of reviews using LLM
- Creates organized tables:
enriched_productsandenriched_reviews
-
RESPOND: Creates an intelligent agent that can answer natural language questions
CREATE AGENT amazon_reviews_agent USING data = {"tables": ['files.enriched_reviews', 'files.enriched_products']};
You can then query the agent:
SELECT answer FROM amazon_reviews_agent
WHERE question = 'What type of product has the best reviews?';
This example shows how MindsDB seamlessly combines SQL with AI to analyze data and provide insights.
Step 4.5: Test the Agent Interface
-
Navigate to Chat Interface Click "Chat with your data" in the left sidebar
MindsDB chat with your data sidebar -
Try the Agent You'll see a chat interface where you can interact with the agent you just created
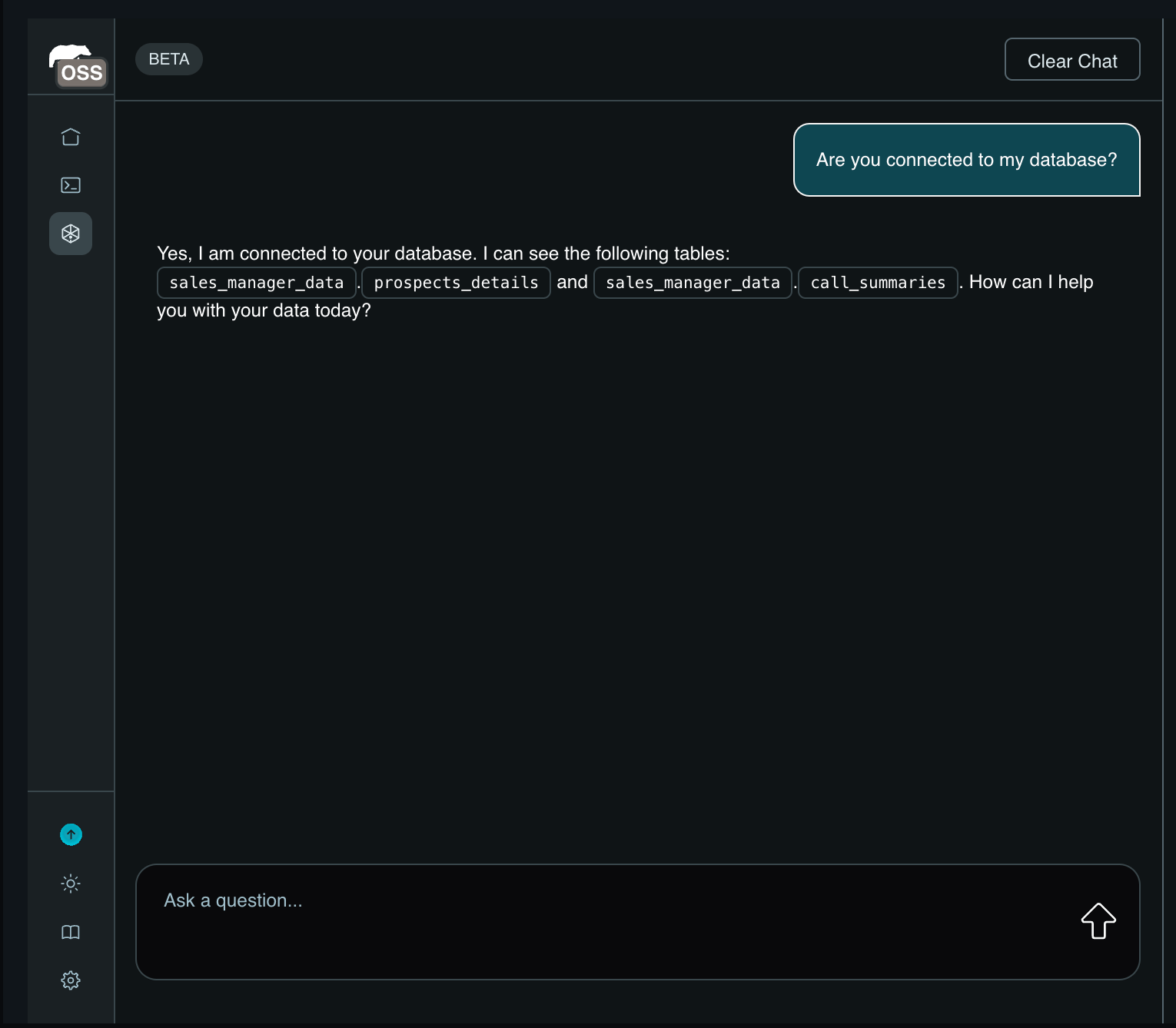
MindsDB chat with data -
Ask Questions Try asking questions like:
- "What products have the most reviews?"
- "Show me the sentiment distribution"
- "Which category has the best ratings?"
✅ Checkpoint: You've successfully set up MindsDB and understand how it works!
Part 5: Connecting Your Robot Database to MindsDB
Now let's connect MindsDB to your actual robot telemetry database.
Step 5.1: Add Your Database Connection
-
Navigate to Onboarding Click "Onboarding" in the left sidebar, then "Connect your data"
-
Select PostgreSQL Search for "PostgreSQL" and click on it

MindsDB select postgres -
Enter Database Credentials Fill in the connection details (same as your
.envfile):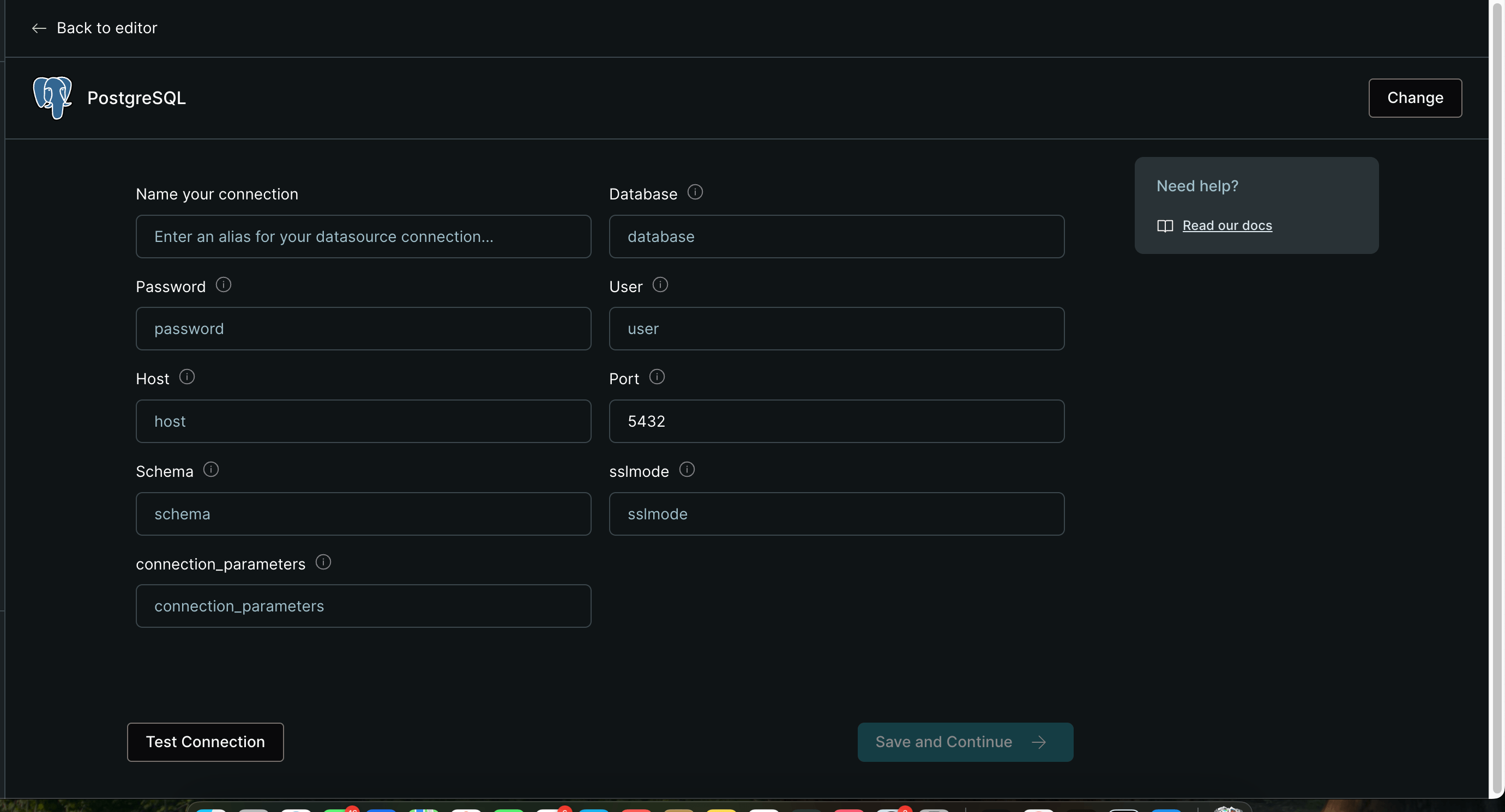
MindsDB set up postgres - Display Name:
robot_postgres_db - Host: Your Vultr server IP
- Port:
5432 - Database:
robot_monitor_db - User:
robot_user - Password: Your database password
- Display Name:
-
Test and Save Click "Test Connection" to verify, then "Save"
Step 5.2: Create a New SQL Script
-
Open SQL Editor Go back to the SQL Editor
-
Create New Tab Click the "+" icon next to "Hello World"
MindsDB select new datasource 
MindsDB new datasource -
Name Your Script Call it something like "Robot Monitor Setup"
Step 5.3: Set Up Your Robot Monitoring System
Copy and paste the contents of mindsdb_setup.sql into the SQL Editor. This comprehensive script will:
📁 View the complete MindsDB setup script:
mindsdb/mindsdb_setup.sql
Step 1: Connect to PostgreSQL (if you didn't do it via UI)
CREATE DATABASE robot_postgres_db
WITH ENGINE = "postgres",
PARAMETERS = {
"user": "robot_user",
"password": "your_password",
"host": "your_vultr_ip",
"port": "5432",
"database": "robot_monitor_db"
};
Step 2: Create Anomaly Detection View This view automatically filters for problematic readings:
- Battery level < 20% (low battery warning)
- Temperature > 80°C (overheating warning)
It also assigns severity levels (CRITICAL, WARNING, OK) and categorizes issues.
CREATE VIEW anomalous_robots AS
SELECT
timestamp,
robot_id,
battery_level,
temperature_celsius,
status_code,
CASE
WHEN battery_level < 10 OR temperature_celsius > 90 THEN 'CRITICAL'
WHEN battery_level < 20 OR temperature_celsius > 80 THEN 'WARNING'
ELSE 'OK'
END as severity,
CASE
WHEN battery_level < 20 AND temperature_celsius > 80 THEN 'Low Battery + High Temperature'
WHEN battery_level < 20 THEN 'Low Battery'
WHEN temperature_celsius > 80 THEN 'High Temperature'
ELSE 'Normal'
END as issue_type
FROM robot_postgres_db.robot_telemetry
WHERE battery_level < 20 OR temperature_celsius > 80
ORDER BY timestamp DESC;
Step 3: Create Gemini AI Model This model generates human-readable maintenance reports:
CREATE MODEL gemini_robot_reporter
PREDICT report
USING
engine = 'gemini',
model_name = 'gemini-pro',
prompt_template = 'You are an expert robot maintenance analyst...';
The prompt instructs Gemini to provide:
- Severity assessment (Low/Medium/High/Critical)
- Root cause analysis
- Immediate action steps
- Recommended action (CONTINUE_OPERATION / SCHEDULE_MAINTENANCE / RETURN_TO_BASE / EMERGENCY_STOP)
Step 4: Generate AI Reports Query that combines anomalies with AI analysis:
SELECT
a.timestamp,
a.robot_id,
a.battery_level,
a.temperature_celsius,
a.severity,
a.issue_type,
g.report as ai_maintenance_report
FROM anomalous_robots AS a
JOIN gemini_robot_reporter AS g
LIMIT 5;
This is where the magic happens! The JOIN operation sends each anomaly to Gemini, which returns a detailed maintenance report.
Step 5: Store Reports Creates a persistent table to save AI-generated reports for historical analysis:
CREATE TABLE files.robot_anomaly_reports (
SELECT ... FROM anomalous_robots AS a JOIN gemini_robot_reporter AS g
);
Step 6: Useful Queries The script includes helpful queries like:
- Get the most recent anomaly with AI report
- Count anomalies by type and severity
- Monitor critical issues in real-time
- Run the Script Click the green "RUN" button and wait for it to complete (may take 30-60 seconds)
✅ Checkpoint: Verify the connection works:
SELECT * FROM robot_postgres_db.robot_telemetry
ORDER BY timestamp DESC
LIMIT 10;
You should see your robot telemetry data!
Part 6: Creating the Intelligent Agent
Now let's create an agent that can answer natural language questions about your robot fleet. In AI hackathons, a demo where you can ask "Which robot needs attention?" and get a natural language answer is a strong differentiator.
Step 6.1: Create the Agent
-
Navigate to Agents In the left sidebar, hover over the "Agents" folder
-
Create New Agent Click the three dots (...) and select "Create Agent"
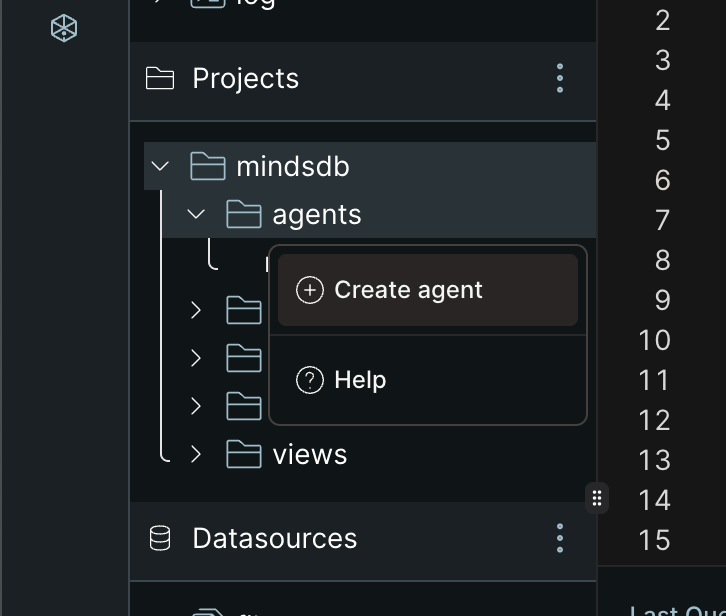
MindsDB Create an Agent -
Add Agent Code Replace the default code with the contents of
create_agent.sql:
📁 View the agent creation script:
mindsdb/create_agent.sql
-- ============================================================================
-- CREATE ROBOT MONITORING AGENT
-- ============================================================================
-- This agent can answer natural language questions about robot telemetry data
-- and anomalies using Google Gemini AI.
--
-- Prerequisites:
-- 1. robot_postgres_db connection created
-- 2. anomalous_robots view created
-- 3. Gemini API key configured in MindsDB Settings
-- ============================================================================
CREATE AGENT robot_monitor_agent
USING
data = {
"tables": [
"robot_postgres_db.robot_telemetry",
"anomalous_robots"
]
};
-- Verify agent was created successfully:
SHOW AGENTS;
What This Does:
The agent is given access to two data sources:
robot_postgres_db.robot_telemetry- All historical robot dataanomalous_robots- Filtered view of problematic readings
When you ask a question, the agent:
-
Understands your natural language query
-
Translates it into SQL queries
-
Retrieves relevant data
-
Formulates a human-readable answer using Gemini
-
Run the Script Click "RUN" to create the agent
Step 6.2: Chat with Your Agent
-
Navigate to Chat Interface Click "Chat with your data" in the left sidebar

MindsDB chat with your data sidebar -
Select Your Agent On the right sidebar under "Agents", click on "robot_monitor_agent"
MindsDB select agent -
Start Asking Questions Try these example prompts:
Basic Status Queries:
- "What is the current status of ROBOT-001?"
- "Show me the latest 5 readings"
- "What's the average battery level over the last hour?"
Anomaly Analysis:
- "How many anomalies occurred today?"
- "List all critical issues from the past 24 hours"
- "What types of failures are most common?"
- "Show me robots with temperature above 85°C"
Predictive Maintenance:
- "Should we schedule maintenance for ROBOT-001?"
- "Which robot needs attention most urgently?"
- "Are there any patterns in the anomalies?"
Statistical Queries:
- "What's the battery drain rate?"
- "Show me the temperature trend over time"
- "Calculate uptime percentage for ROBOT-001"
Complex Questions:
- "Compare battery performance before and after anomalies"
- "What's the correlation between temperature and status code?"
- "Summarize robot health for the past week"
The agent will analyze your data and provide intelligent, context-aware answers!
Part 7: Testing Your System End-to-End
Let's verify everything is working together.
Test Scenario 1: Low Battery Alert
-
Wait for Low Battery Let your simulator run until battery drops below 20%
-
Query for Anomalies In MindsDB SQL Editor:
SELECT * FROM anomalous_robots WHERE issue_type = 'Low Battery' ORDER BY timestamp DESC LIMIT 3; -
Get AI Analysis
SELECT a.robot_id, a.battery_level, a.severity, g.report FROM anomalous_robots AS a JOIN gemini_robot_reporter AS g WHERE a.issue_type = 'Low Battery' ORDER BY a.timestamp DESC LIMIT 1; -
Verify Gemini Response The report should recommend "RETURN_TO_BASE" or "SCHEDULE_MAINTENANCE"
Test Scenario 2: High Temperature Alert
Since temperature anomalies are randomly injected, you might need to wait or temporarily increase ANOMALY_PROBABILITY in your .env file.
-
Check for Temperature Anomalies
SELECT * FROM anomalous_robots WHERE issue_type = 'High Temperature' ORDER BY timestamp DESC LIMIT 3; -
Ask the Agent In the chat interface: "Are there any overheating issues?"
Test Scenario 3: Agent Intelligence
Ask progressively complex questions:
- "How many total readings do we have?"
- "What percentage are anomalies?"
- "Should I be concerned about ROBOT-001's performance?"
- "Create a maintenance schedule recommendation"
Troubleshooting
Simulator Won't Connect to Database
Error: Failed to connect to database
Solutions:
- Verify Vultr firewall allows port 5432
- Check
.envhas correct IP address - Confirm PostgreSQL is running:
sudo systemctl status postgresql - Test connection manually:
psql -h your_vultr_ip -U robot_user -d robot_monitor_db
MindsDB Can't Query Database
Error: Database connection timeout
Solutions:
- Verify the connection details in MindsDB match your
.env - Check that PostgreSQL allows remote connections (Step 2.6)
- Ensure
pg_hba.confincludes the0.0.0.0/0rule
Gemini Model Not Working
Error: Model prediction fails
Solutions:
- Verify API key is correct in MindsDB Settings
- Check you have Gemini API credits remaining
- Ensure model name is exactly
gemini-pro - Try recreating the model with a simpler prompt
No Anomalies Showing Up
Issue: anomalous_robots view is empty
Solutions:
- Let simulator run longer (anomalies are random)
- Temporarily increase
ANOMALY_PROBABILITYin.envto 0.5 (50%) - Manually verify thresholds:
SELECT * FROM robot_telemetry WHERE battery_level < 20;
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I use this robot monitoring stack in an AI hackathon?
You can use it as your main project: deploy the simulator and database, connect MindsDB and Gemini, and demo the chatbot answering questions about robot health. Judges often like seeing real-time data, AI-generated reports, and a natural language interface in one place.
Is this tutorial suitable for beginners in AI hackathons?
Yes. The steps are sequential and we use Docker and managed-style setup where possible. If you're new to AI hackathons, pair with someone who knows SQL or Python, or focus on Parts 1–3 first and add the AI agent (Parts 4–6) once the pipeline works.
What are some AI hackathon project ideas using this stack?
Ideas include: multi-robot fleet dashboard, predictive maintenance alerts, a "robot health assistant" chatbot, or extending the simulator to represent drones, AGVs, or IoT sensors. You can also theme it for healthcare, logistics, or smart factories.
How long does it take to complete this for an AI hackathon?
Setting up Vultr, PostgreSQL, the simulator, and MindsDB typically takes 1–2 hours. Adding the Gemini reporter and agent is another 30–60 minutes. Plan for a half-day to have a stable demo, plus time to customize for your hackathon theme.
Are there any limitations when using this in time-limited hackathons?
The main constraints are: you need a Vultr account (and possibly a small budget), a Gemini API key, and Docker. In short AI hackathons, consider running PostgreSQL and MindsDB locally first, then moving to Vultr if you have time. The simulator can run on a laptop and still demo the full flow.
What You've Built
Congratulations! You've created a production-ready AI-powered monitoring system:
✅ Cloud Infrastructure: PostgreSQL database hosted on Vultr ✅ Real-time Data Pipeline: Python simulator generating realistic telemetry ✅ AI Integration: MindsDB connecting Gemini AI to your database ✅ Anomaly Detection: Automated filtering and severity classification ✅ Natural Language Reports: AI-generated maintenance recommendations ✅ Intelligent Chatbot: Agent that answers questions about your robot fleet
Next Steps & Improvements
Immediate Enhancements
- Multiple Robots: Modify simulator to create
ROBOT-002,ROBOT-003, etc. - Email Alerts: Set up notifications when critical anomalies occur
- Web Dashboard: Build a React/Vue frontend to visualize data
- Scheduled Reports: Create daily maintenance summaries
Advanced Features
- Predictive Maintenance: Use MindsDB's built-in ML models to predict failures
- Historical Analysis: Train models on past data to detect patterns
- Slack Integration: Send alerts to a Slack channel
- Custom Metrics: Add motor speed, location tracking, task completion rate
- Multi-database Support: Connect to MongoDB, MySQL, or other data sources
- Real-time Dashboard: Use WebSockets for live updates
Production Readiness
- Authentication: Secure your MindsDB and PostgreSQL with proper auth
- SSL/TLS: Enable encrypted connections
- Backup Strategy: Set up automated database backups
- Monitoring: Add Grafana or Prometheus for system metrics
- Load Testing: Simulate 100+ robots to test scalability
To put this into practice in a time-boxed setting, join an online AI hackathon on LabLab.ai and build your robot monitor as your project.
Learning Resources
- Full project code: smart-robot-monitor-with-AI-alerts – simulator, database schema, MindsDB scripts, and config files
- MindsDB Documentation: docs.mindsdb.com
- Gemini API Reference: ai.google.dev
- Vultr Tutorials: vultr.com/docs
- PostgreSQL Guide: postgresql.org/docs
🎉 You did it! You've successfully built an AI-powered robot monitoring system from scratch. This architecture can be adapted for IoT devices, server monitoring, vehicle fleets, or any system that generates time-series data and needs intelligent analysis.
Happy building!


